Carbohydrates come from nearly all foods in your diet and eventually break down into glucose You need glucose, the simplest form of carbohydrates, to provide energy to every cell in your body Carbohydrates break down into sugars, like glucose, which provide fuel for muscle contraction and other processes These processes occur along your digestive tract Once broken down, these smaller elements find their way into your body's cells, where they combine with enzymes to perform any number of your body's functions, includingWhen we eat foods that contain carbohydrates the body needs to break these down into simple monosaccharides for the body to use The digestion process of polysaccharides such as starch will begin in the mouth where it is broken down or 'hydrolysed' by salivary amylase an enzyme in your saliva that helps to break down starches

Why Do You Need Food Food Provides Your Body With Materials To Grow And Repair Tissues It Provides Energy For Everything You Do Your Body Breaks Down Ppt Video Online Download
What does carbohydrates break down into
What does carbohydrates break down into-Catabolism is the set of metabolic processes that break down large molecules These include breaking down and oxidizing food molecules The purpose of catabolic reactions is to provide the energy and components needed by anabolic reactions Carbohydrate catabolism is the breakdown of carbohydrates into smaller units Carbohydrates areNutrition Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are basically sugar and starch Apples, oranges, potatoes, grains, candy, bread are all carbohydrates Carbohydrates break down into glucose molecules When used as energy, carbohydrates fuel become fuel for your muscles and brain If your body does not have any use for the glucose, it is converted




Food And Energy Why You Need Food Food
Starches, which are found in foods such as starchy vegetables (like potatoes or corn), grains, rice, breads, and cereals; Amylolytic enzymes break down carbohydrates Specifically, amylolytic enzymes break down complex carbs (polysaccharides) into simple sugars like glucose Interestingly, these enzymes are used commercially to produce beer, food sweeteners, and paper Amylase is one of the most common amylolytic enzymes It's considered a pancreatic enzymeCarbohydrates (also called carbs) are a type of macronutrient found in certain foods and drinks Sugars, starches and fiber are carbohydrates Other macronutrients include fat and protein Your body needs these macronutrients to stay healthy How does the body process carbohydrates?
When carbohydrates are broken down into glucose within the blood, the body will Use insulin to help fuel the body's cells ;Substrate level phosphorylation 11 In glycolysis, a molecule of glucose is split into 2 molecules of PGAL These molecules are ultimately converted into 2 pyruvic acid molecules Both simple and complex carbohydrates break down into glucose (aka blood sugar) A simple carb is one that's comprised of one or two sugar molecules, while a complex carb contains three or more
When healthy complex carbs are consumed your body breaks them down into glucose to use as fuel or to store in muscles as glycogen When your body has a sufficient amount of glucose and glycogen fuel your body will run properly When you look for complex carbs to put into your body, take a look at fibrous and starchy carbs Fibrous Carbs Once complex starch molecules are broken down into glucose, THEN they enter your bloodstream through the intestine So even though the digestive process of simple and complex carbohydrates differs, the end result is the same SUGARThe two main forms of carbohydrates are sugars such as fructose, glucose, and lactose;
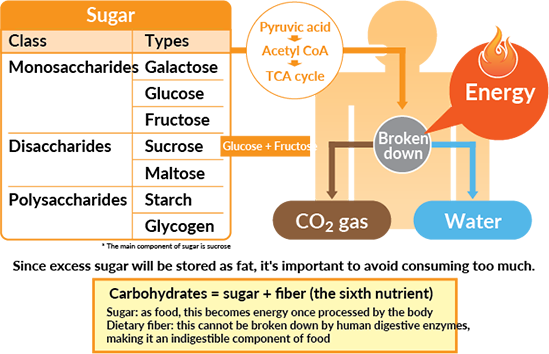



Carbohydrates An Efficient Energy Source Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co Ltd




How The Human Body Break Down And Digest Food Britannica
During digestion, carbohydrates are broken down into simple, soluble sugars that can be transported across the intestinal wall into the circulatory system to be transported throughout theYour digestive system breaks down carbs into glucose or bloodDuring digestion, carbohydrates are broken down into simple, soluble sugars that can be transported across the intestinal wall into the circulatory




Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii



Carbohydrate Protein And Lipids Are The Three Main Chegg Com
When those energy demands increase, carbohydrates are broken down into constituent monosaccharides, which are then distributed to all the living cells of an organism Glucose (C 6 H 12 O 6 ) is a common example of the monosaccharides used for energy productionThese different components can have different effect on your blood sugar levels and overall health, but are all defined as carbohydrates The amount of total carbohydrates in a serving of food corresponds to the sum of starches, sugars and dietary fiber When digested, digestive enzymes break down starches into single units of glucose Sucrase breaks sucrose into glucose and fructose molecules Maltase breaks the bond between the two glucose units of maltose, and lactase breaks the bond between galactose and glucose Once carbohydrates are chemically broken down into single sugar units they are then transported into the inside of intestinal cells



15 3 Digestive System Processes Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition



Carbohydrates
Plus, our bodies have evolved to break down complex carbs into simpler components, including mono and disaccharides, he says In other words, even when you eat complex carbs, simple carbs end up These carbohydrates need longer to break down into glucose and provide you the most nutrients in addition to calories Refined carbohydrates are considering as bad carbohydrates, they processed to remove some parts of grains such as fibers Most common refined (processed) carbohydrates are white bread, cookies, biscuits, pastries, and allComplex carbohydrates These carbohydrates are composed of long strings of simple carbohydrates Because complex carbohydrates are larger molecules than simple carbohydrates, they must be broken down into simple carbohydrates before they can be absorbed If more protein is consumed than is needed, the body breaks the protein down and



1




Food And Energy Why You Need Food Food
When you eat food that contains carbohydrates, you break down the carbohydrates into a monosaccharide called Via what process are these ATP molecules made?When people eat a food containing carbohydrates, the digestive system breaks down the digestible ones into sugar, which enters the blood As blood sugar levels rise, the pancreas produces insulin, a hormone that prompts cells to absorb blood sugar for energy or storage As cells absorb blood sugar, levels in the bloodstream begin to fallUse insulin to turn any remaining excess of glucose in the blood into fat for storage ;



Q Tbn And9gcrngedmz5p8ksahkx4mevekwbdzyga0f I1kthrenssnk8u Lpe Usqp Cau
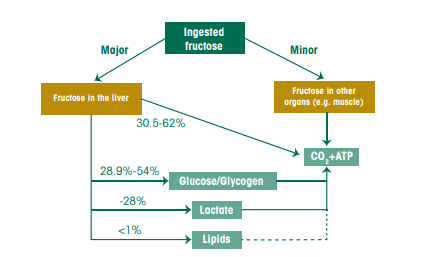



Carbohydrate Digestion And Absorption The Canadian Sugar Institute
•During _____, a series of enzymatic reactions break down the carbohydrates in these foods into simple carbohydrates that are easily absorbed in the small intestine digestion Complex carbs require these enzymes for digestionBreak down carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, into small molecules that can be moved into the circulatory system Digestive enzymes carbohydrates In some cases, entering the pathway simply involves breaking a glucose polymer down into individual glucose moleculesThe body breaks down or converts most carbohydrates into the sugar glucose



The Worst Food You Can Eat On A Fat Loss Journey Juggy Sidhu




Carbohydrate Quality And Human Health A Series Of Systematic Reviews And Meta Analyses The Lancet
Get smart on carbs When you eat or drink foods that have carbohydrate—also known as carbs—your body breaks those carbs down into glucose (a type of sugar), which then raises the level of glucose in your blood Your body uses that glucose for fuel to keep you going throughout the day This is what you probably know of as your "bloodNormally your enzymes break carbohydrates down into glucose (a type of sugar) If you have one of these disorders, you may not have enough enzymes to break down the carbohydrates Or the enzymes may not work properly This causes a harmful amount of sugar to build up in your body That can lead to health problems, some of which can be serious Carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars that are used by the body for energy As carbohydrates are eaten, the digestive tract breaks them down into monosaccharide units, or glucose The glucose enters the bloodstream and travels first to the brain, which runs entirely on energy from glucose




The Physiology Of Fasting Zero




Carbohydrate Metabolism Wikipedia
Most carbohydrates, except fiber, are ultimately broken down into sugars, and these sugars are responsible for giving you the energy your body needs to power through your dayCarbohydrates provide energy and therefore if you have too high a level of carbohydrate in your diet this can lead to weight gain It ultimately breaks down all digestible carbs into glucose, one of the simplest carbohydrates and the body's primary fuel Some tissues, such as the brain, red blood cells, kidneys, cornea, testes
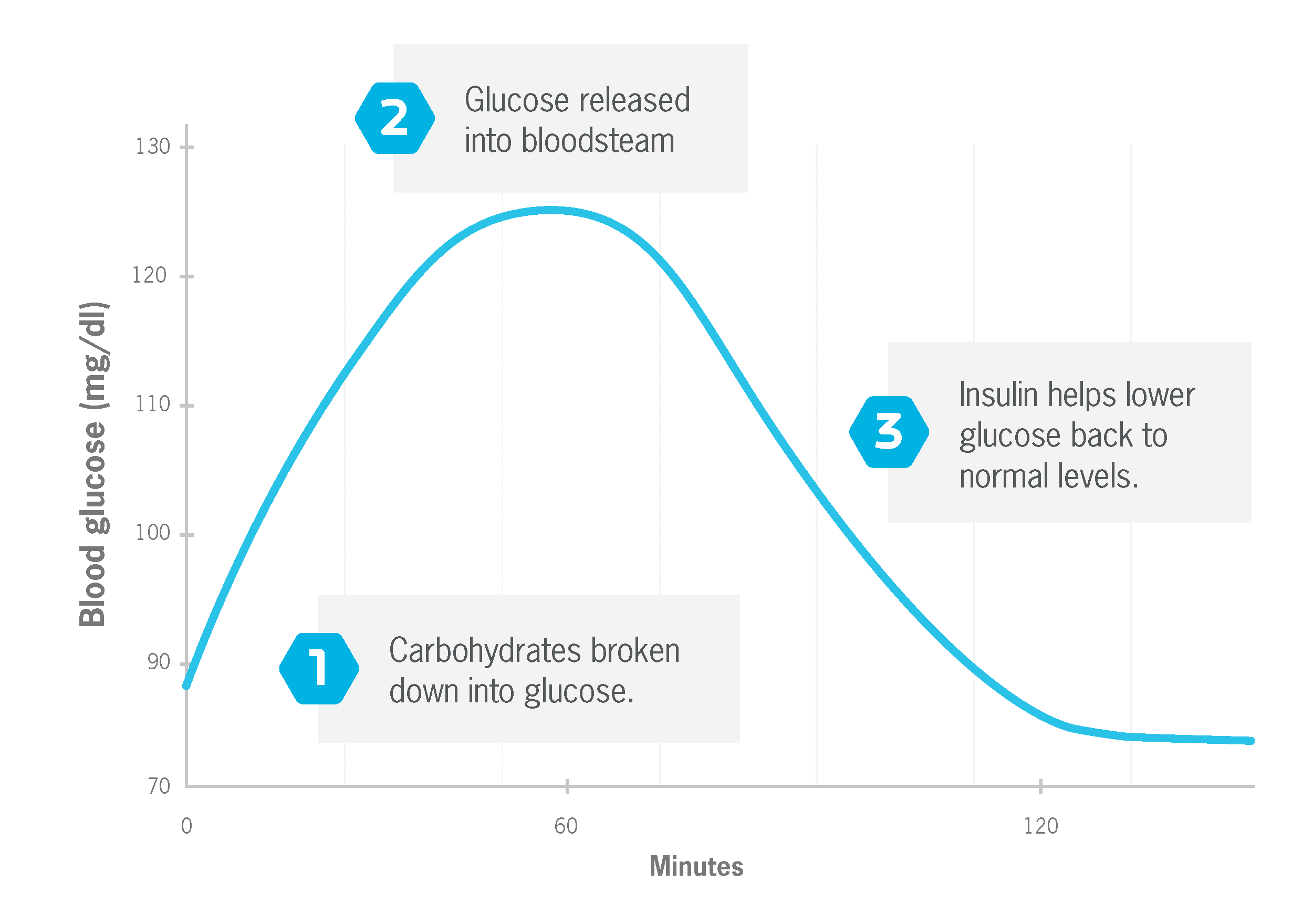



The Truth About Carbs Insulin And Weight Loss Precision Nutrition
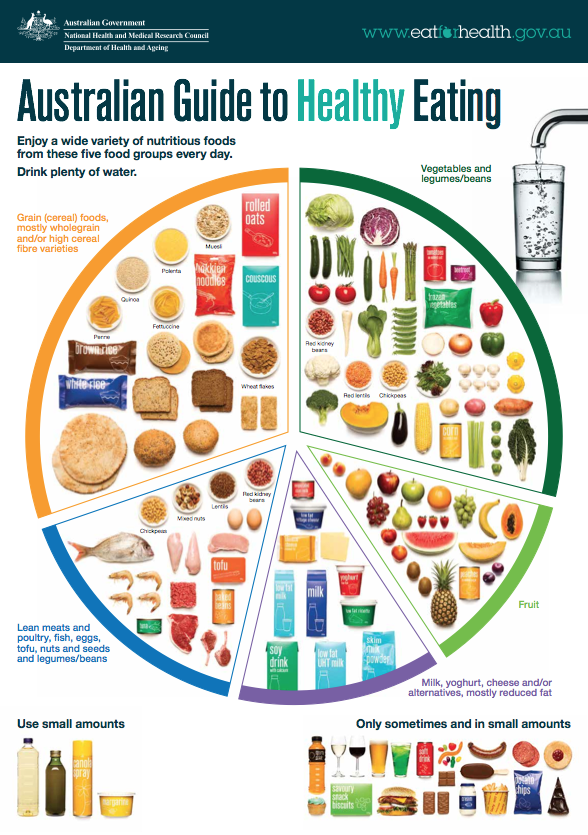



Carbohydrates Healthy Kids
Once absorbed carbohydrates pass through the liver, glucose is the main form of carbohydrate circulating in the bloodstream 4 Large Intestine or Colon Any carbohydrates that weren't digested in the small intestine mainly fiber pass into the large intestine, but there's no enzymatic digestion of these carbohydrates hereCarbohydrates travel through the esophagus, stomach and enter the small intestine In the small intestine, carbohydrates get further broken down into single carbohydrate units called monosaccharide These single molecules get absorbed across the intestine wall and are sent through the blood stream Although maltose is a simple sugar, when it reaches the intestine, the intestinal enzymes further break it down into glucose These glucoses molecules then enter the blood stream from the intestine Fiber is also a complex carbohydrate, but it is different because it does not get broken down in the body to glucose
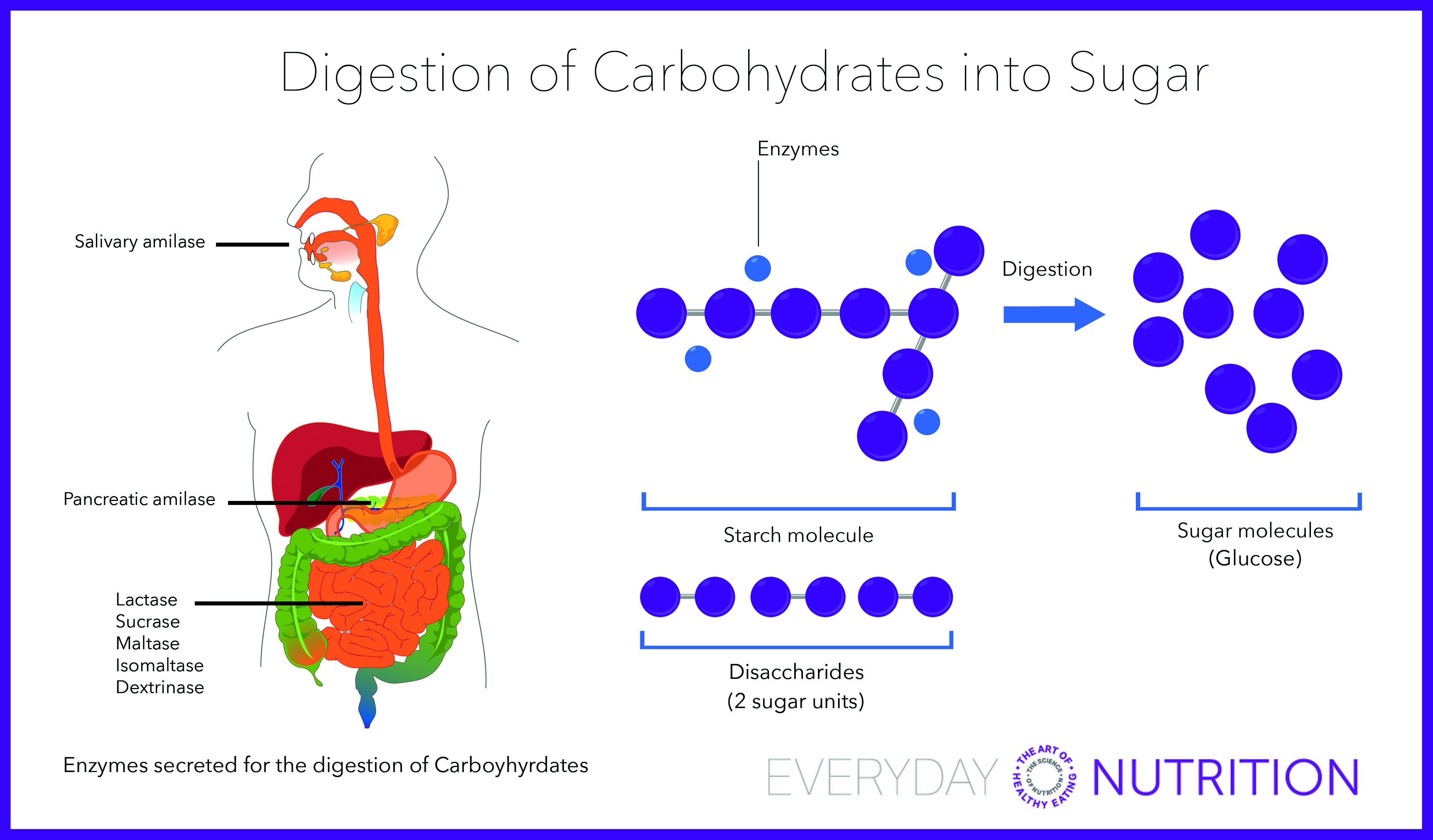



Everyday Nutrition Digestion Of Carbohydrates Into Sugar



Types Of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are broken down by the body into glucose, which can be absorbed into the bloodstream Once absorbed, glucose molecules travel in However, the body can still break them down fairly easily into simple sugars and finally into glucose, the simple sugar that the body uses directly for energy The chemical composition of carbohydrates is a nice starting point, but the real information you probably want to know about carbs is how they are used by the body These types of carbohydrates should be the primary source of carbohydrates in your diet Fibre – A Protective Carbohydrate Fibre is a special type of carbohydrate because the body cannot break it down into its simple sugar molecules Fibre is also responsible for making you feel fuller, longer



Carbohydrate Digestion Gastrointestinal Medbullets Step 1




Defining Carbohydrates Fats And Protein Fitivate
The body converts these sugar molecules into glucose, which it uses for energy As complex carbohydrates have longer chains, they take longer to break down and provide more lasting energy in the The process of carbohydrate break down starts in our mouth with an enzyme called salivary amylase It breaks the long sugars apart into smaller subunits to be absorbed, and these small, simple carbohydrates move through the cell lining of the small intestine and into the blood in capillaries that lead to the portal veinSucrase breaks sucrose into glucose and fructose molecules Maltase breaks the bond between the two glucose units of maltose, and lactase breaks the bond between galactose and glucose Once carbohydrates are chemically broken down into single sugar units they are then transported into the inside of intestinal cells




3 3 Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates Medicine Libretexts




Basic Guide To Eating Right Nutrition Metabolism Build Up And Break Down Of Tissues In Your Body A Fast Metabolism Means You Can Absorb And Use Nutrients Ppt Download
Carbohydrates are used for energy (glucose) Fats are used for energy after they are broken into fatty acids Protein can also be used for energy, but the first job is to help with making hormones, muscle, and other proteins After a meal, the blood sugar (glucose) level rises as When you ingest carbohydrates your body will go to work to break it down into its simplest form, this is called glucose Glucose is the "food" that's delivered to your body's cells, tissues and organs Food = fuel, right?




Simple Vs Complex Carbohydrates Difference Between Simple Sugars And Starches




Nutrient Metabolism Human Learn Science At Scitable




Absorption Of Carbohydrates Ppt




All About Carbohydrates Types Role Metabolism Requirements




Into What Substance Do Most Carbohydrates Break Down During Digestion Study Com




Carbohydrates And Blood Sugar The Nutrition Source Harvard T H Chan School Of Public Health
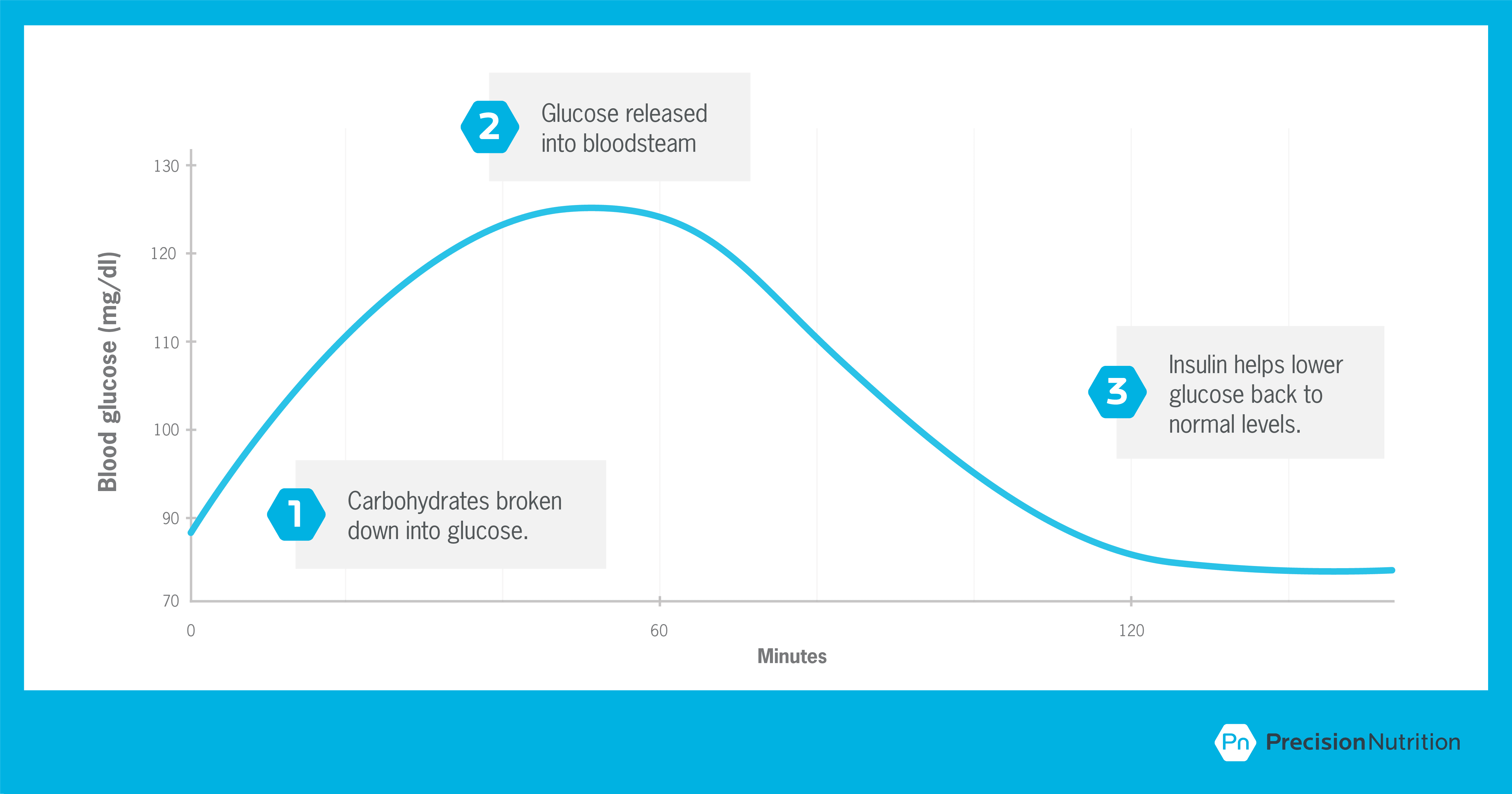



The Truth About Carbs Insulin And Weight Loss Precision Nutrition




Good Vs Bad Carbs 10 Sources Of Healthy Carbs That Actually Support Weight Loss Clean Food Crush




9 Absorption Of Carbohydrates Amino Acids And Lipids Flashcards Quizlet




Monosaccharides Disaccharides Polysaccharides Sugars Starches




Carbohydrates Your Body S Most Important Source Of Fuel Everyday Health




Breaking Down The Carbohydrate From Simple To Complex




Carbohydrate Digestion Absorption Enzymes Process And More



Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates




Digestive System Processes Biology For Majors Ii




Carbohydrates American Heart Association
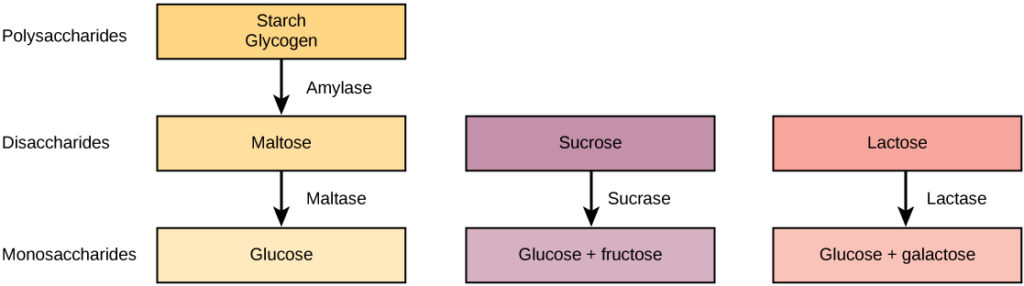



Digestive System Processes Biology For Majors Ii




Carbohydrates Definition Formula Classification Importance Examples




Why Do You Need Food Food Provides Your Body With Materials To Grow And Repair Tissues It Provides Energy For Everything You Do Your Body Breaks Down Ppt Video Online Download
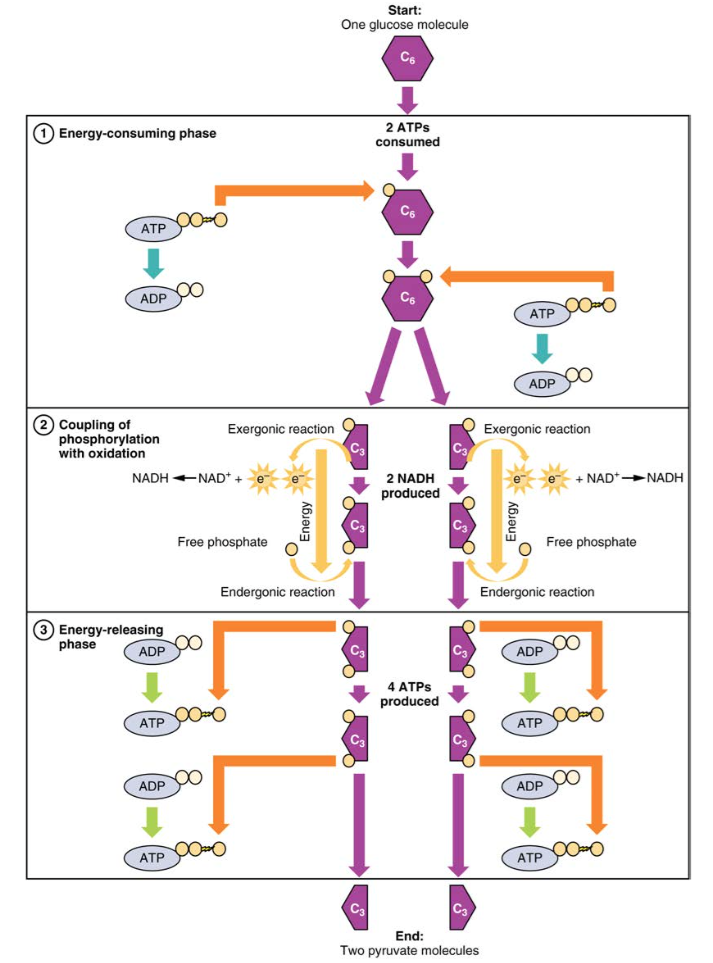



Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/simple-and-complex-carbohydrates-and-diabetes-1087570-ADD-FINAL-V2-d27e373ab541449ba70bb26ff5f7cf71.png)



What To Know About Simple Vs Complex Carbohydrates




Carbohydrates Sugar Starch And Fiber Ppt Video Online Download
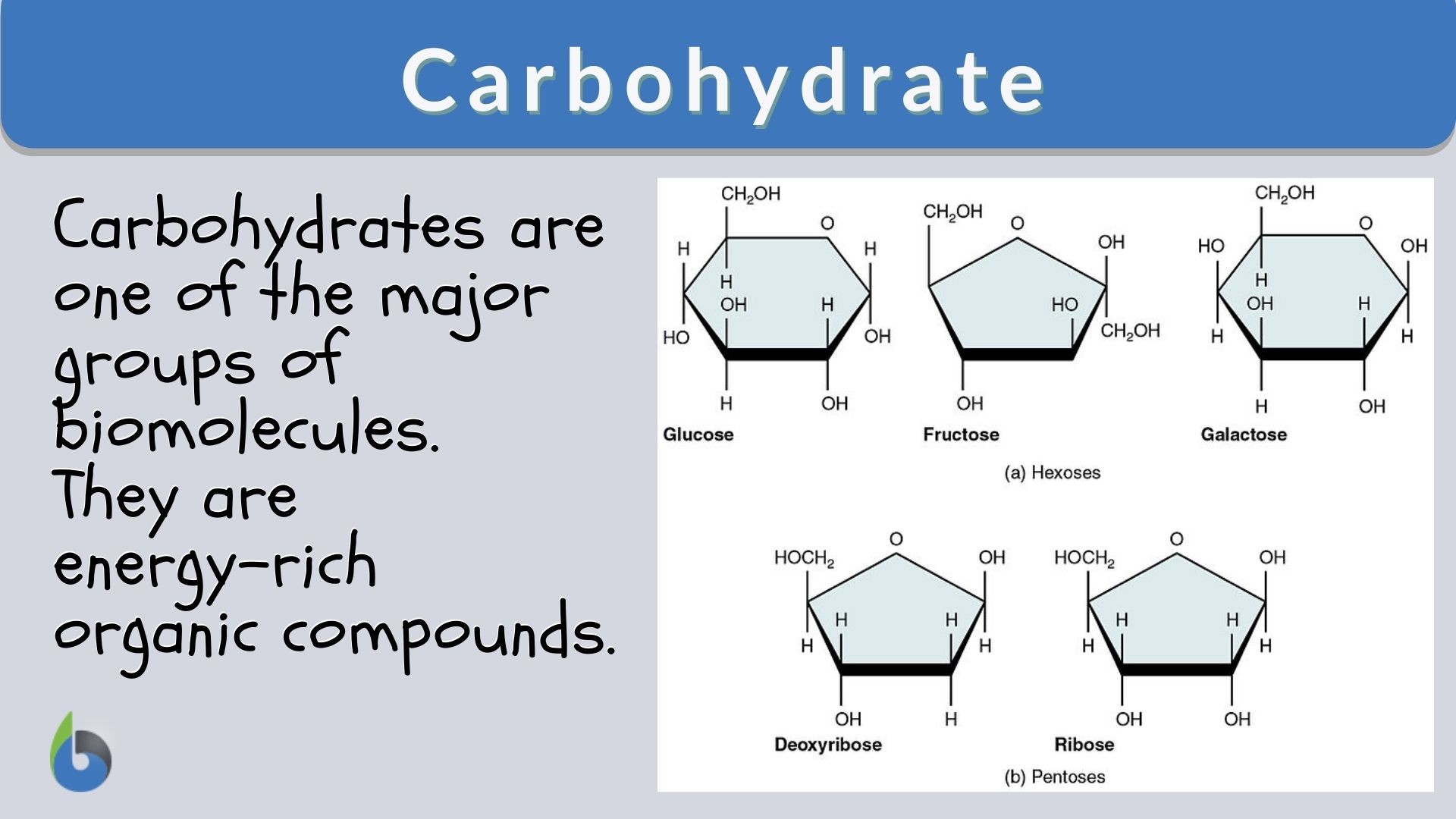



Carbohydrate Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary




Lecture 13 General Characteristic Of The Carbohydrates Their



Carbohydrates How Food Works Howstuffworks




Rohit Vats What Is Ketosis Most People Think Facebook
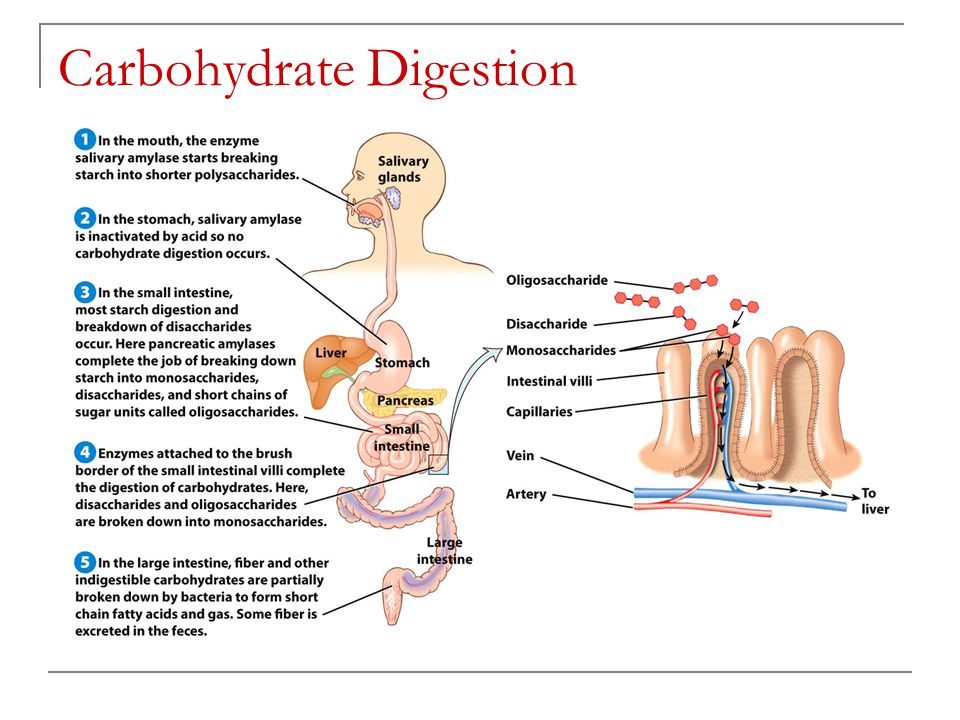



Chapter 4 Carbohydrates Sugar Starches And Fiber Ppt Video Online Download



Science Storyboard Storyboard Por 18hayerg



Understanding The Body S Digestive System Hello Miss Niki




An Introduction To The Digestive Enzymes Questions Digestion Stomach
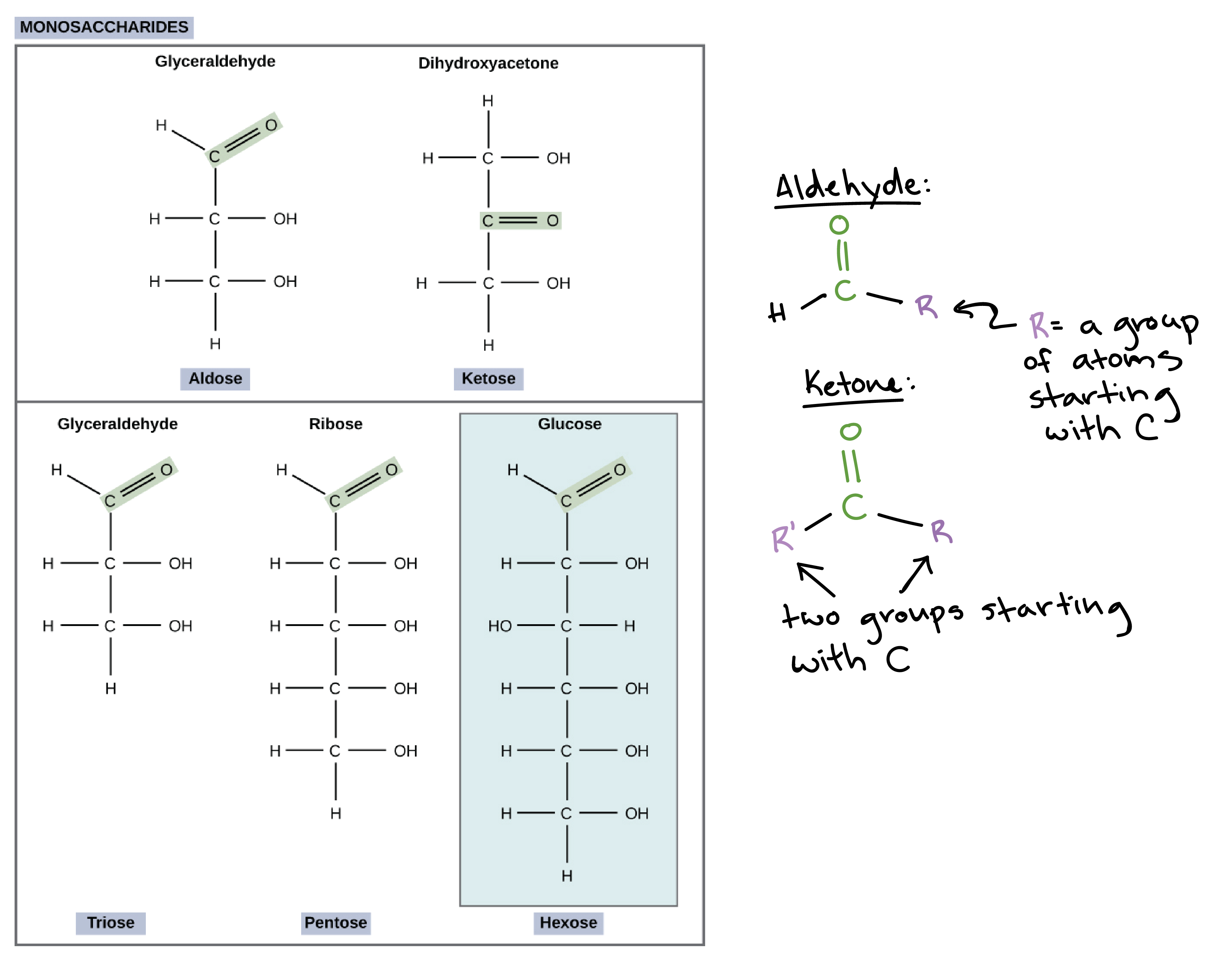



Carbohydrates Article Chemistry Of Life Khan Academy
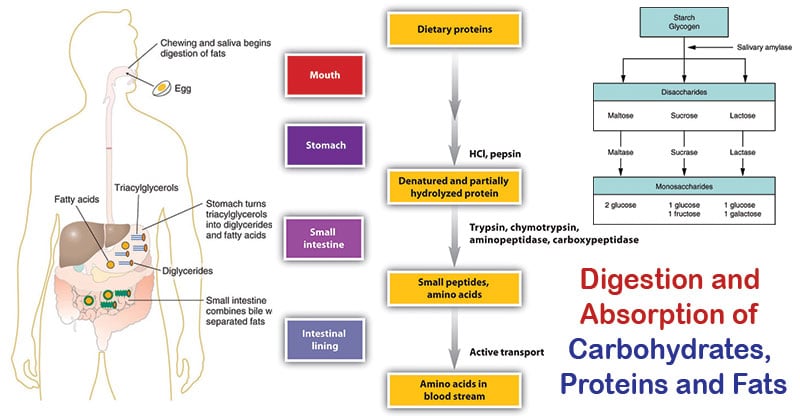



Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates Proteins And Fats
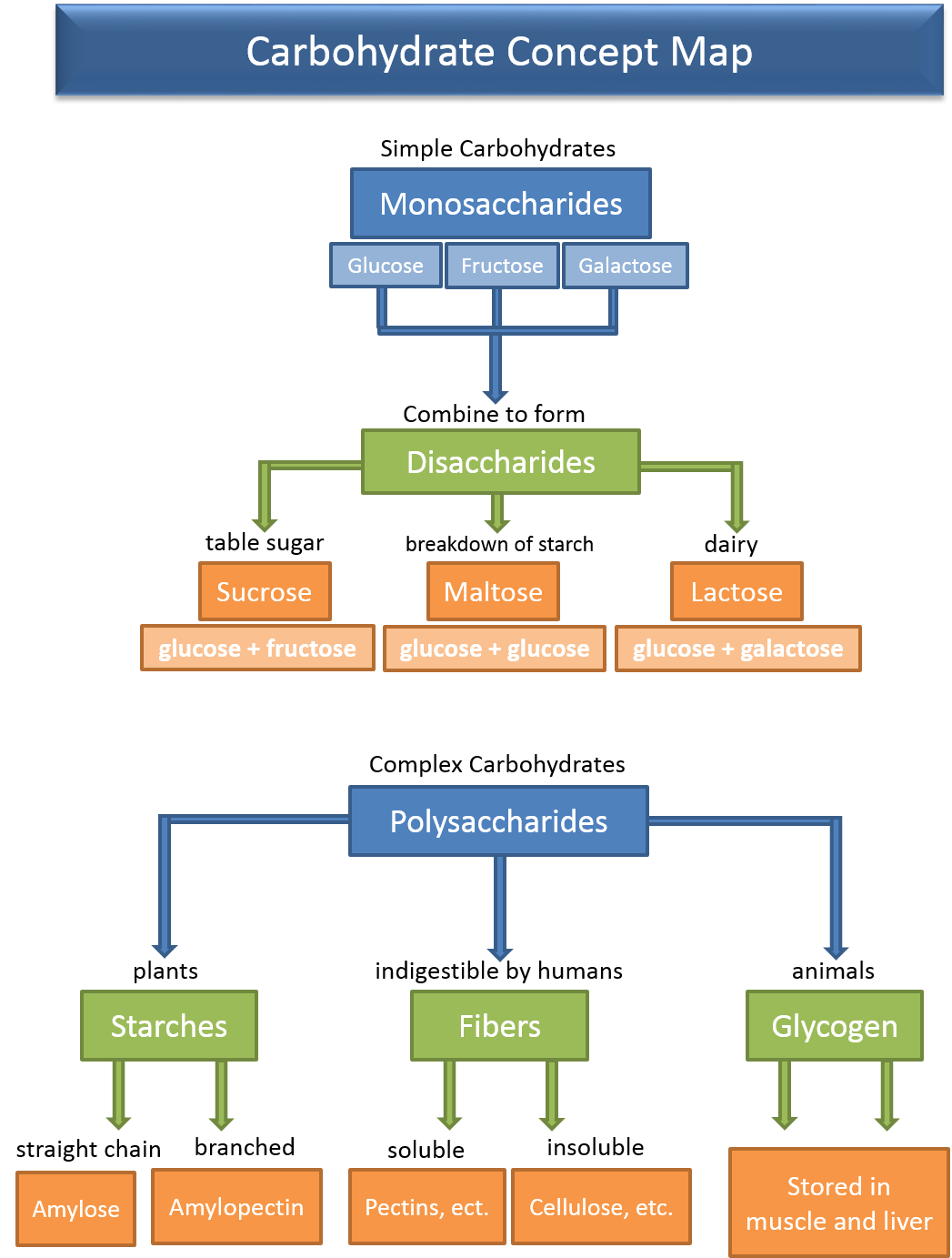



Carbohydrates



15 3 Digestive System Processes Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
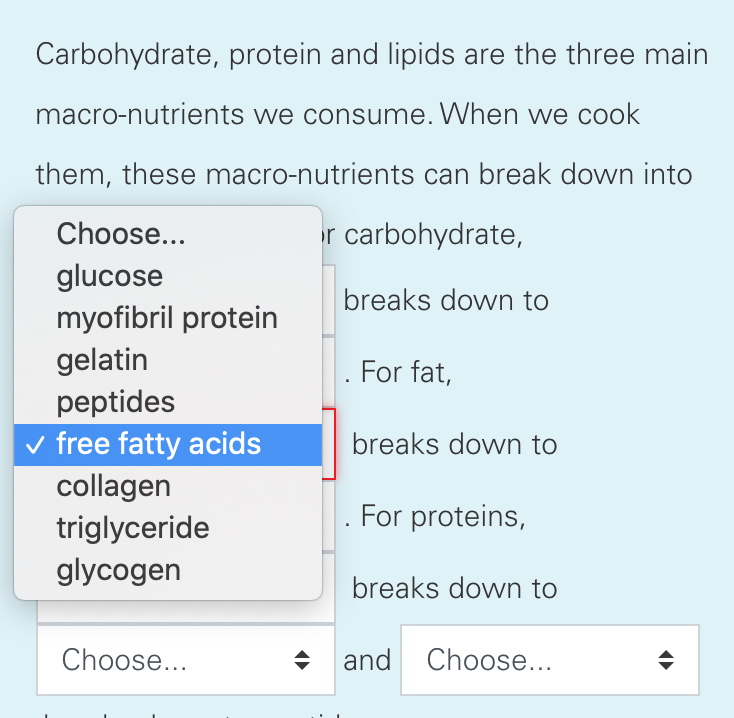



Carbohydrate Protein And Lipids Are The Three Main Chegg Com




Biology Lecture One The Chemistry Of Organic Molecules




Carbohydrates Proteins And Fats Ders Of Nutrition Msd Manual Consumer Version Pdf Glycemic Index Carbohydrates




Carbohydrate Their Types And Sources Carbohydrates Youtube



Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates




Carb Vs Sugar How To Understand Nutrition Labels




Carbohydrates Uses Health Benefits Nutrition And Risks



Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates Human Nutrition Deprecated




Carbohydrate Metabolism




Nutrition Ja Ro Dw Alk Er Carbohydrates Most



Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates Human Nutrition Deprecated




Carb Vs Sugar How To Understand Nutrition Labels



Www Naspghan Org Files Documents Pdfs Training Curriculum Resources Physiology Series Carbohydrate Digestion Naspghan Pdf




Carbohydrates
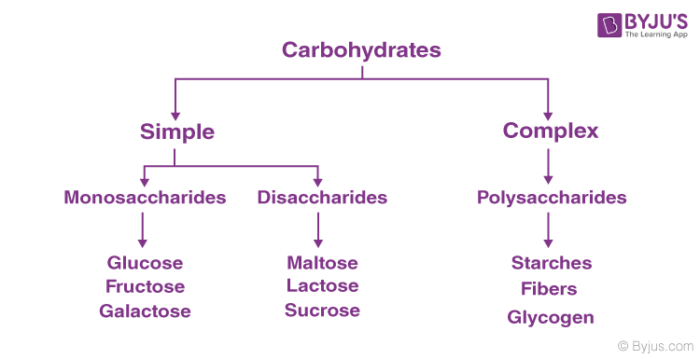



Classification Of Carbohydrates With Definition Types Structure Formula With Examples Videos




Simple Carbs Vs Complex Carbs What S The Difference




And Through A Series Of Chemical Reactions Break Down These Carbohydrates Into Simple Sugars Functions Of Pancreatic Juice 1 Bicarbonate Ions Hco Ppt Download




Carbohydrates Docsity




Carbohydrate Definition Classification Examples Britannica




Process Of Digestion Digestion Process In Mouth Stomach Intestines
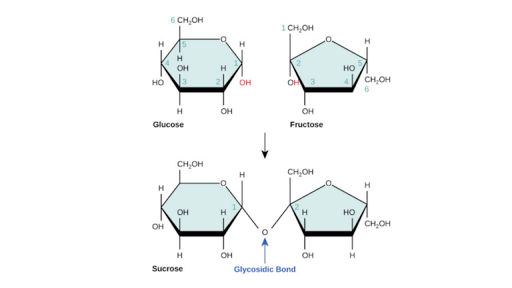



Carbohydrates Article Chemistry Of Life Khan Academy



1
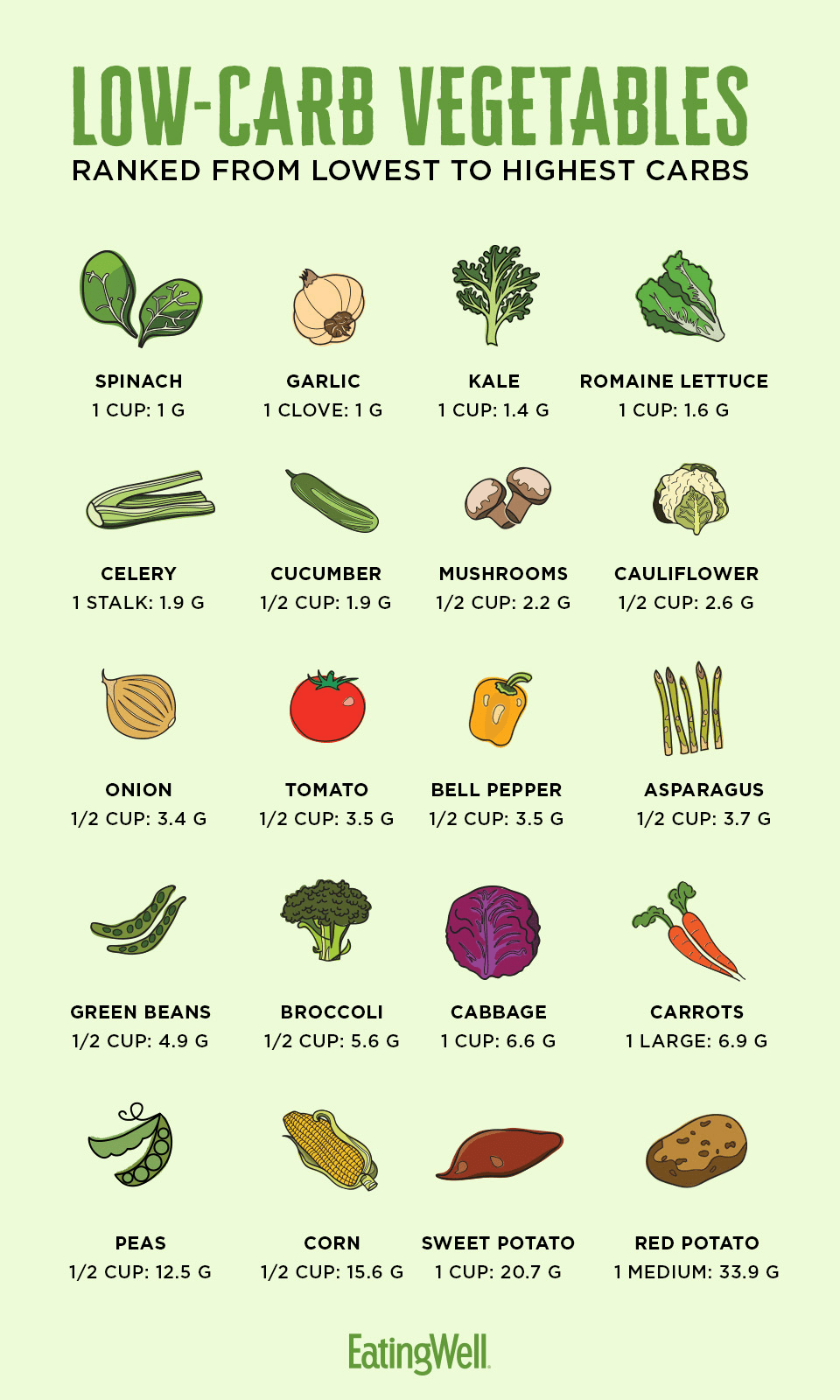



How Many Carbs Are In Vegetables Eatingwell




Simple Carbs Vs Complex Carbs What S The Difference




What Are Carbohydrates Live Science
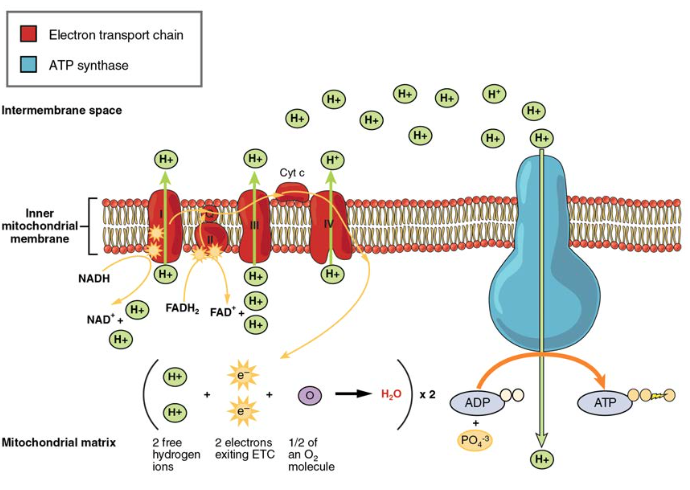



Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii



Www Naspghan Org Files Documents Pdfs Training Curriculum Resources Physiology Series Carbohydrate Digestion Naspghan Pdf
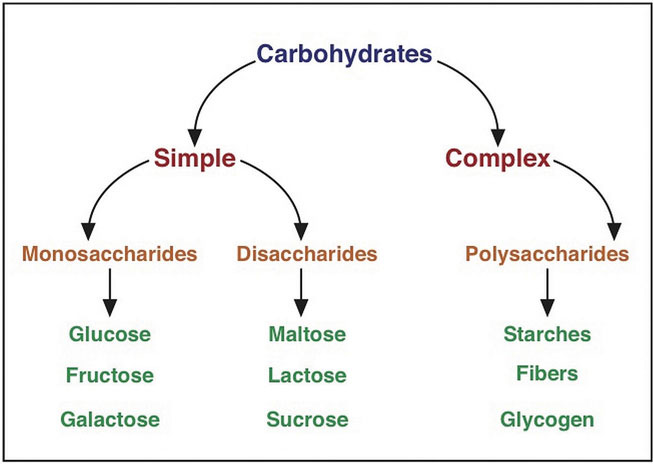



A Closer Look At Carbohydrates




Solved Part A The Process Of Carbohydrate Digestion Begin Chegg Com
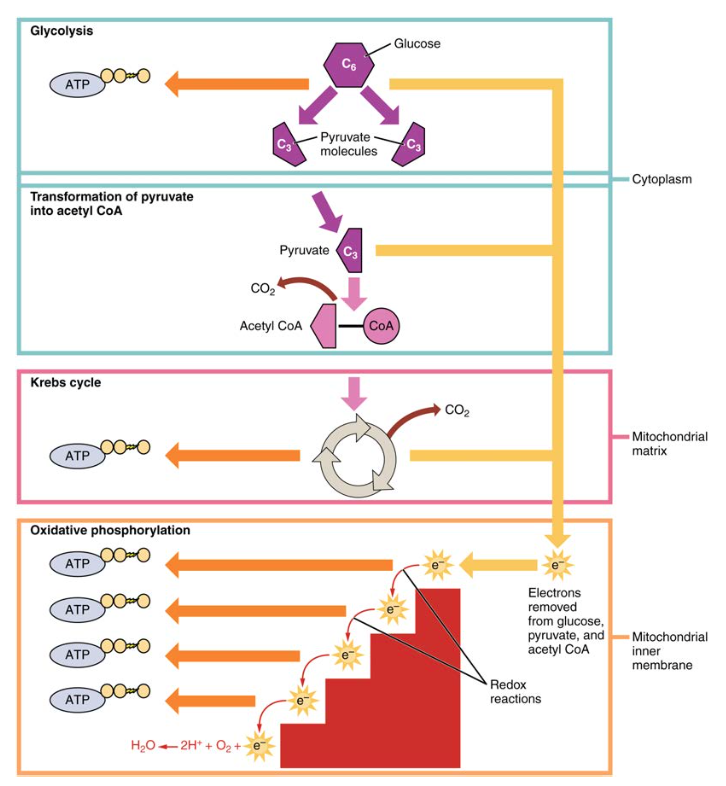



Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii




Carbohydrate Definition Classification Examples Britannica




3 3 The Digestion And Absorption Process Medicine Libretexts




What Are Carbs Everything You Need To Know About Carbohydrates
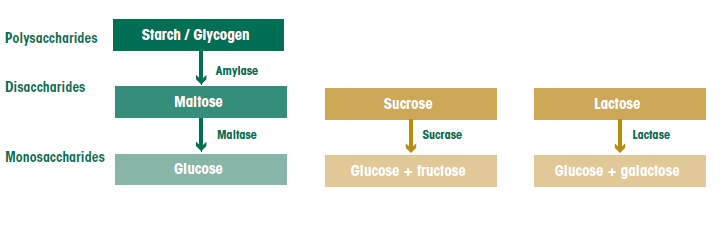



Carbohydrate Digestion And Absorption The Canadian Sugar Institute




Digestion Absorption And Transport In Digestive System




3 3 Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates Medicine Libretexts




Carbohydrate Digestion Absorption Enzymes Process And More



Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates
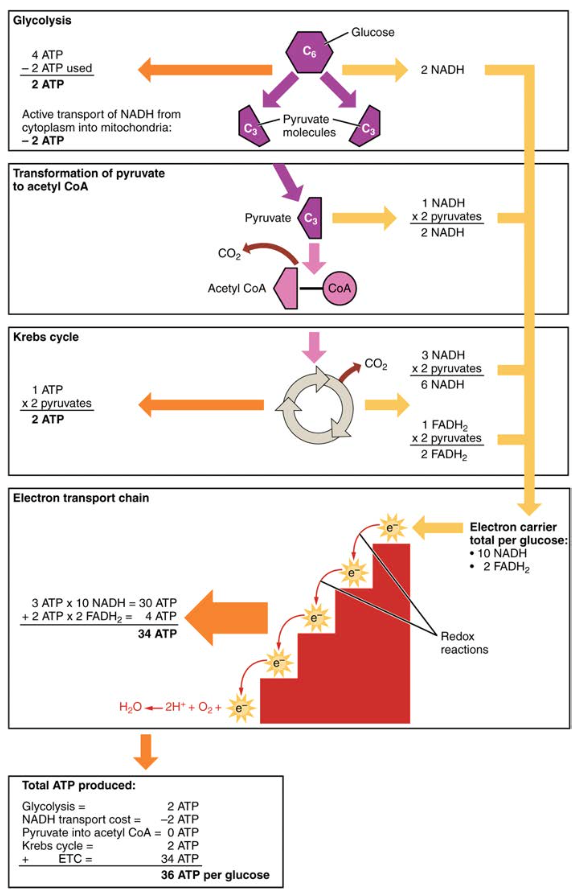



Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii




What Are The Key Functions Of Carbohydrates



1




Carbohydrates Uses Health Benefits Nutrition And Risks




This Flow Chart Shows The Steps In Digestion Of Carbohydrates The Different Levels Shown Are Starch Carbohydrates Biology Biology Notes Anatomy And Physiology
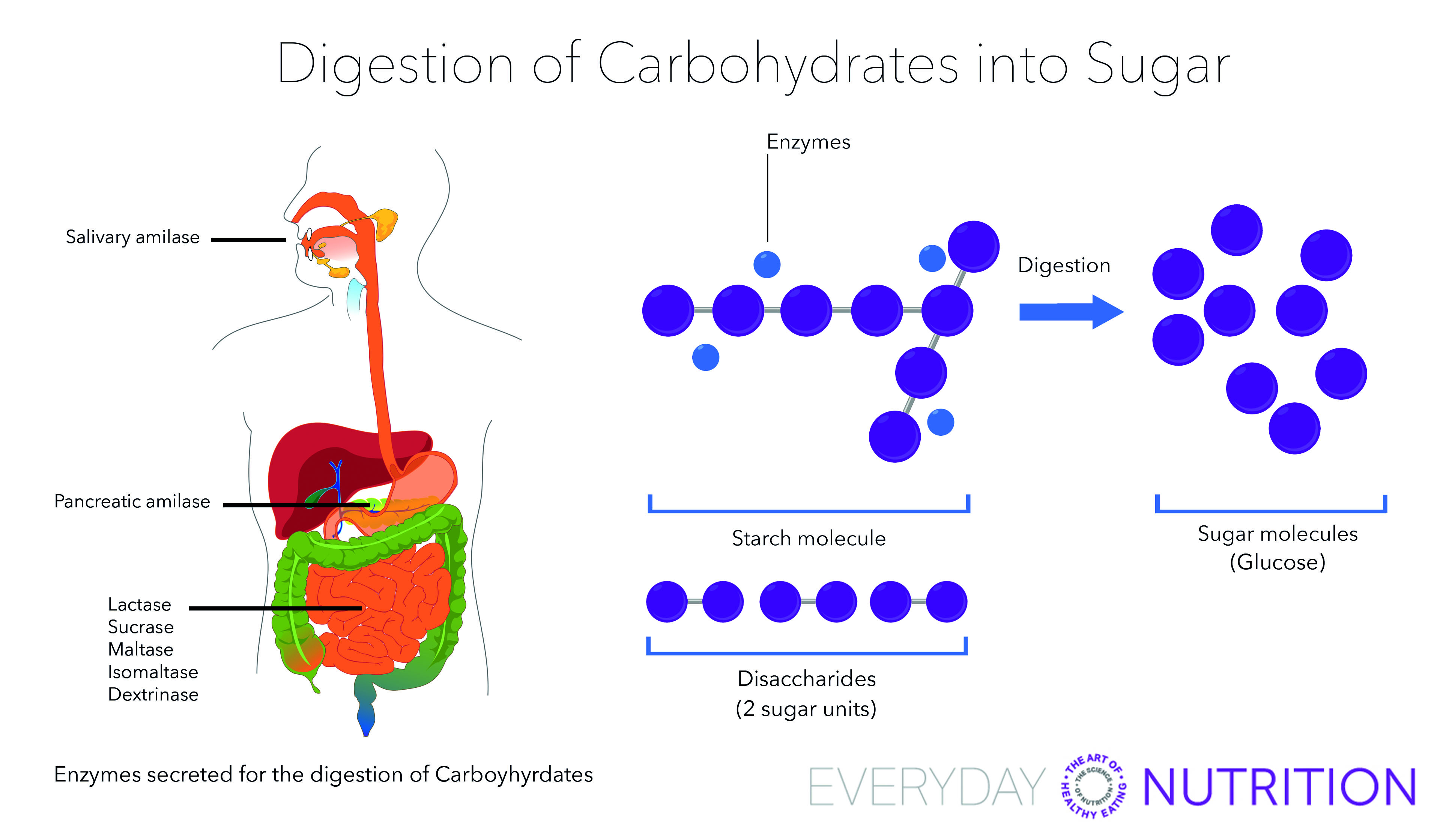



Everyday Nutrition Digestion Of Carbohydrates Into Sugar



Carbohydrates Nutrition For Animals




What Do Carbohydrates Taken In As Food Break Down Into




The No Bs Guide To Good Healthy Carbs




The Importance Of Complex Carbohydrates In Your Diet



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿